Sustainable Governance
永續治理
Optimizing Mechanisms and Fostering Culture to Strengthen Risk Management
In recent years, the global landscape has become increasingly volatile. Risks are rising across multiple areas, as factors like rapid advancement of AI, fluctuating raw material prices, geopolitical conflicts, geo-economic rivalries, tariff disputes, along with changing sustainability and environmental regulations can all impact project cost, schedule, and quality. In response, CTCI is committed to strengthening its risk management by continually refining mechanisms, fostering a strong risk-aware culture among all employees, and enhancing organizational resilience, which helps lay a solid foundation for sustainable governance.
Optimizing Risk Management Mechanisms
In response to rapidly changing business conditions, the Company continues to review and enhance its risk management mechanisms. The following summarizes recent improvements.
Project Risk: Enhancing Oversight during the project proposal stage
1.Authorization Adjustment
The Group's authorization control mechanism has been revised. In addition to the existing authorization supervisors corresponding to different bid amounts, the authorization levels have been adjusted for mechanisms such as gate review, high-risk projects, and those exceeding the risk threshold. This strengthens the review and decision-making mechanism, thereby controlling and reducing bidding risks.
2.Launching new Gate Review control mechanism
To enhance risk management in the project proposal stage, a new Gate Review control mechanism has been established. It clearly defines requirements for each gate, and all projects under tender are now managed in accordance with the Gate Review control regulations. Two key control items are introduced in the chart below:

3. Supervision and Management of Subsidiaries
To strengthen the management of proposal tendering risks for overseas subsidiaries, relevant regulations have been added to the group SOP. These include the requirement that, upon receiving local tender information, overseas subsidiaries must promptly notify the responsible CTCI business unit according to the tender’s business attributes. The head of the business unit will evaluate the project and then report to the CEO of the Group Engineering Business (GEB). Only after obtaining the GEB CEO's approval may the overseas subsidiaries proceed with the subsequent Gate Review process.
Corporate Operational Risk: preventing confidential data leaks
To safeguard the intellectual property rights of all companies within the Group, minimize the risk of infringement, and prevent the leakage of confidential information, a series of measures have been implemented in recent years. These include: prohibiting the use of USB devices; protecting electronic files of confidential documents through online access controls, confidentiality warnings, and mandatory online signing of confidentiality declarations for SOP; hard drive encryption; requiring all employees to sign the Letter of Undertaking to CTCI Corporation’s Policies on Confidentiality and Intellectual Property Rights; conducting regular evaluations of intellectual property (IP) protection awareness among Group employees; and ensuring confidentiality and intellectual property return agreements for departing employees.
This year, we further enhanced our confidential information monitoring and exception control mechanisms, establishing a Data Leakage Prevention (DLP) system to monitor internal and external information transmission. The DLP system monitors potential information leaks through internal and external email, internet browsing, or social media uploads. When anomalies are detected, immediate notifications are issued and dedicated personnel are assigned to asses and investigate the incident, ensuring appropriate follow-up actions are taken to prevent recurrence. Furthermore, CTCI obtains TIPS certification in 2024, demonstrating its commitment to daily maintenance and risk control of intangible assets such as intellectual property.
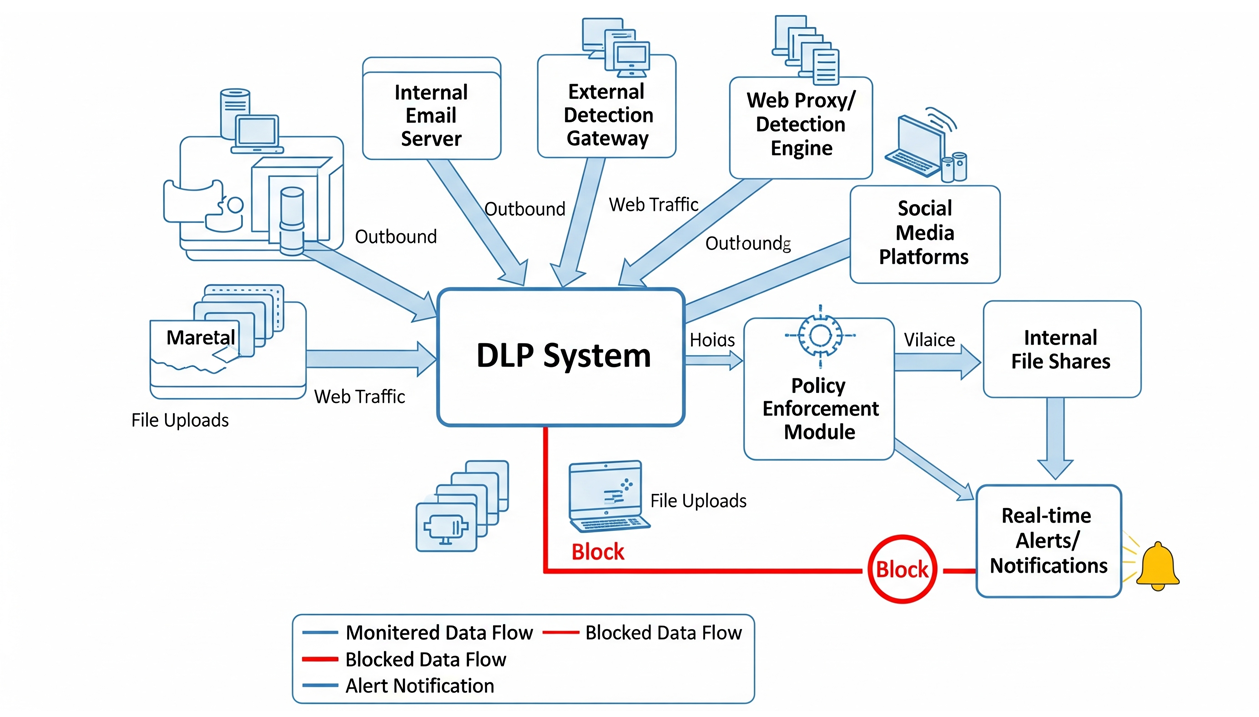
Diagram showing the DLP system
Climate and Nature Risk: import climate and natural risk assessment methods
To respond to the international attention and development trend on biodiversity issues, CTCI has imported the TCFD (Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures) and TNFD (Task Force on Nature-related Financial Disclosures) frameworks to assess and disclose climate and natural risks and opportunities, and to deeply integrate practical processes. Specific actions include:
1.Imported the latest climate scenarios and LEAP methodology: Using the latest UN climate scenarios to understand future climate trends, and utilizing the LEAP (Locate, Evaluate, Assess, and Prepare) method to master natural dependencies and impacts, we conducted a comprehensive climate and natural risk inventory for our operation locations and project sites for the first time, thereby mitigating risks and proactively planning for business development opportunities.
2.Leveraging Core Business Influence: Through green engineering, such as energy-saving and carbon-reduction technologies, circular economy models, and eco-friendly measures, we can not only reduce the impact on the ecological environment but also develop transformational business opportunities.
3.Independently issue TCNFD reports: Not only has TCFD and TNFD information been incorporated into the sustainability report, but TCNFD reports have also been issued annually since 2024 to ensure information transparency.
4.Collaborate with value chain partners: Promote environmental risk management with suppliers and work with upstream and downstream companies to ensure the sustainability of the supply chain.
Moreover, the scope of climate and nature risk and nature-related financial disclosures has been expanded from CTCI Corporation to the CTCI Group. The "Group Climate and Nature Risk Management Regulations" have been revised to institutionalize this approach. The responsibilities of relevant departments and managers at all levels are clearly defined, and regular reporting is required to the Board of Directors and the Sustainability and Information Security Committee to ensure compliance with the company's sustainability strategy.
Strengthening Organizational Risk Mindset
To build and strengthen a comprehensive risk culture, managers at all levels regularly raise employee’s’ awareness of risk management standards and procedures. This helps ensure staff understand the they Group's risk policies and risk control requirements, and apply them in their daily work. In addition, annual Group-wide risk management training in organized for supervisors at different levels and employees across the organization to further enhance risk awareness. Recent training activities as following: All members of the group: Group Risk Management Requirement Awareness Training To establish a basic understanding of risk management among all employees, the "Group Risk Management Requirements Awareness Training" has been conducted. The program introduces key concepts of risk and risk management, explains the Group’s related SOPs, roles and responsibilities, policies, and control measures, and helps employees understand the fundamental requirements so they can apply them effectively in their work. General management: Lecture on "Essential Legal Concepts for Projects Execution” and "Legal Risks and Responses in Project Execution" To strengthen legal awareness and enhance legal and risk planning capabilities at the management level, a senior lawyer specializing in engineering law was invited to deliver lectures on "Essential Legal Concepts for Projects Execution” and "Legal Risks and Responses in Project Execution". Top management: Special Lecture To address current risk issues, external experts are invited to share their latest insights. Recently, specialists in risk and control delivered lectures to directors and senior executives on "Mastering the AI Risk Management Framework and Enhancing Trust in Integrated AI Applications" and "Understanding Future Market Trends Through Global Economic Changes". These session help leadership stay informed on emerging trends and strengthen their ability to respond to risks.



Conclusion
CTCI commissioned SGS Taiwan(Société Générale de Surveillance, SGS)to conduct an ISO 31000 Risk Maturity assessment audit, through which it received the highest recognition of the “Role Model”. The result affirmed that CTCI’s continued efforts on risk management, along with its well-established mechanisms, have reached international standards and laid a solid foundation for stable operations and sustainable development. CTCI believes that a sound and proactive risk management framework is not only essential for enhancing global competitiveness but also critical in effectively responding to increasingly complex internal and external risks and challenges.

CTCI Corporation underwent an ISO 31000 audit in 2024, received a “Role Model” rating from SGS, and demonstrated its world-class risk management capabilities.

