Sustainable Governance
永續治理
From New Standards to a New Future: Upgrading Information Security Resilience
According to the Global Risks Report 2024 published by the World Economic Forum (WEF), information security-related issues continue to rank among the top five concerns. In Taiwan, government and authorities are placing increasing emphasis on information security issues; there are growing demands for the establishment and strengthening of information security controls across a range of entities, including government agencies, state-owned enterprises, financial institutions, and publicly listed companies. This clearly indicates that information security and compliance have become universal challenges across industries.
Adapting to International Standards: Comprehensive update of Information Security Management System
At the same time, the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) announced its third edition of ISO/IEC 27001:2022 Information Security Management Systems in 2022. CTCI, as an organization already certified under the previous version, must complete the transition to the new version by October 31, 2025, to maintain the validity of its certification.
The most significant changes in this update include the addition of cybersecurity and privacy protection, with new related requirements introduced. Firstly, in terms of information protection, there are now provisions for information deletion, data masking, and data leakage prevention. Secondly, for management of technical vulnerabilities, new requirements for threat intelligence collection and analysis have been added. Observing the adjustments in Annex A of the controls reflects these updates in the new version. These modifications include,
• Control Domains(Themes):The number of domains have been revised from 14 to 4 themes , which include organizational controls, people controls, physical controls, and technological controls.
• Total Number of Controls:Decreased overall 114 controls into 93 controls. Some controls have been merged, others have been removed, new controls have been introduced, and some have been updated.
• Control Attribute Values:5 attributes were introduced including control type, information security properties, cybersecurity concepts, operational capabilities and security domains.
Initiating the Transition: Ongoing Enhancements to Cybersecurity Management
To comply with the requirements of ISO/IEC 27001:2022, CTCI will undertake the following revision activities,
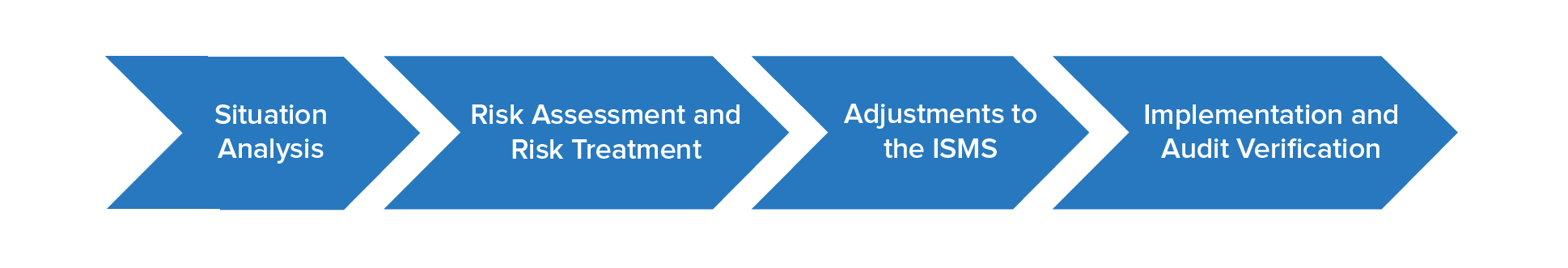
• Situation Analysis:Review and analyze existing security policies, organizational structure, personnel responsibilities, information assets, and operational processes to assess compliance with the new version requirements.
• Risk Assessment and Risk Treatment:Establish a risk assessment procedure that meets the new version requirements and perform risk assessment activities. Based on the results of the risk assessment, carry out risk treatment and ensure that residual risks are controlled to acceptable levels.
• Adjustments to the Information Security Management System(ISMS):Update the Statement of Applicability and adjust existing management documents according to the results of the gap analysis.
• Implementation and Audit Verification:Implement internal audits and conduct reviews and improvements, and complete the annual information security management review to facilitate the successful attainment of certification for the new version.
Through the cycle of Plan-Do-Check-Act (PDCA), an iterative process for continually improving products, people, and services, CTCI will continually improve its information security management system, while also expanding the assessment of alignment with other systems. Furthermore, the principles of ISO/IEC 27001 will be advocated across all subsidiaries of CTCI group to enhance the overall information security resilience and adhere to international quality benchmarks.
**Photo credit: Pixabay




