Sustainable Governance
永續治理
Application of Robotic Process Automation Technologies in Turnkey Projects
In a rapidly changing business environment, staying flexible and efficient is crucial for companies to meet the increasingly complex challenges. CTCI, as an international Engineering, Procurement, and Construction(EPC)turnkey project service provider, understands that the efficiency and transparency of operations in every stage are crucial for a project to success, whether that’s design, procurement or construction. In recent years, the Group has gradually intensified the application of Robotic Process Automation (RPA) technologies into its operations, improving business procedures and governance structures. combining these efforts with the Environmental, Social, and Governance(ESG) initiatives to promote sustainability.
This article will detail how RPA has influenced the Group when applied at all levels of operations, and how it integrates with the governance aspect of ESG standards to drive a sustainable development within the company.
Strengthening Support: The Use of RPA in Corporate Governance and Project Execution
RPA is a technology that uses software robots to mimic and integrate human interactions with information systems to perform highly repetitive, rule-based tasks. RPA can automate various business processes, including data entry, data processing, and compliance checks. By reducing human errors, improving operational efficiency, and unleashing the creativity of employees, RPA allows corporations are to significantly enhance their operational efficiency and quality, further improving the governance efficiency of companies.
Effective corporate governance not only ensures transparency and compliance in daily operations but also helps build the reputation of corporations while developing their capabilities for sustainable governance. For an engineering services provider like CTCI, robust governance is particularly crucial for managing complex projects, leveraging interested parties at all levels, and mitigating potential risks.
Therefore, in recent years, CTCI has been actively designing and developing RPA robots for departments involved in design, procurement, and construction phases. This initiative aims to improve and optimize existing workflows, enhance employee efficiency, and reduce errors. In the current fast-paced engineering environment with limited human resources, the following cases will demonstrate how CTCI has implemented multiple RPA solutions across departments.
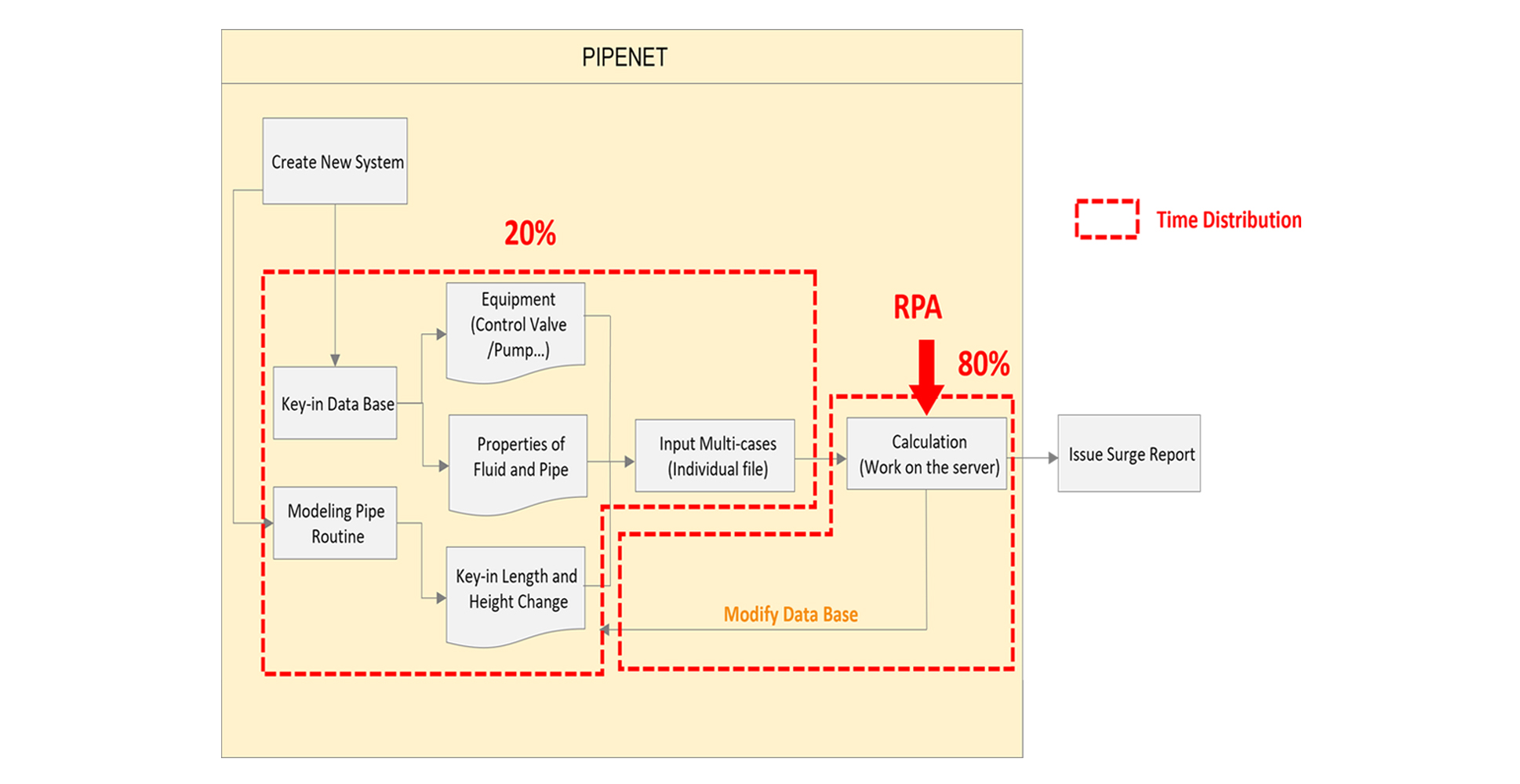
Application One: RPA for PIPENET Automation
PIPENET is a specialized software system used for designing and simulating pipeline networks, widely applied in industries such as oil, natural gas, chemical, and water treatment engineering. Its primary functions include simulating various pipeline design scenarios and generating corresponding data reports to assist engineers in analyzing and optimizing pipeline network systems. Typically, pipeline engineers manually input the designed parameter into the PIPENET software, initiate simulations, and obtain results reports after the simulations are complete.
However, several pain points can be observed during the process:
• Long simulation durations: Due to the complexity of calculations and the large amount of required data, simulations in PIPENET can take a considerable amount of time. The engineers weren’t able to use their time effectively during the waiting period.
• Restricted user numbers: PIPENET software imposes restrictions on simultaneous access on the number of users. During peak usage periods, this limitation can lead to resource constraints, further affecting work efficiency.
• Lack of result notifications: After completing a simulation, PIPENET does not automatically notify users when results are ready. Colleagues must continuously monitor the software's status, resulting in wasted time and effort.
• Manual input errors: There is a possibility of errors during manual parameter input, which can lead to inaccuracies in simulation results and subsequently impact engineering decisions.
The use of RPA technology with a web-based interface can effectively address the aforementioned pain points. Users simply upload design parameter files to the PIPENET Automation web page, and the RPA system takes care of the rest, providing multiple benefits:
• Automated simulation: Once the parameter files are uploaded, the RPA system automatically initiates operations in the PIPENET. RPA can replicate human operational steps, including parameter setting, simulation initiation, and result extraction, ensuring accuracy and consistency at every step.
• Real-time progress monitoring: Users can monitor the progress of simulation in real-time on the PIPENET Automation website. Through a visualized monitoring interface, users can stay informed about progress without needing frequent manual checks.
• Result notifications and report generation: Upon completion of the simulation, the RPA system automatically notifies users via email. This automated notification feature ensures users to receive results promptly, enabling them to proceed with further analysis and design tasks.
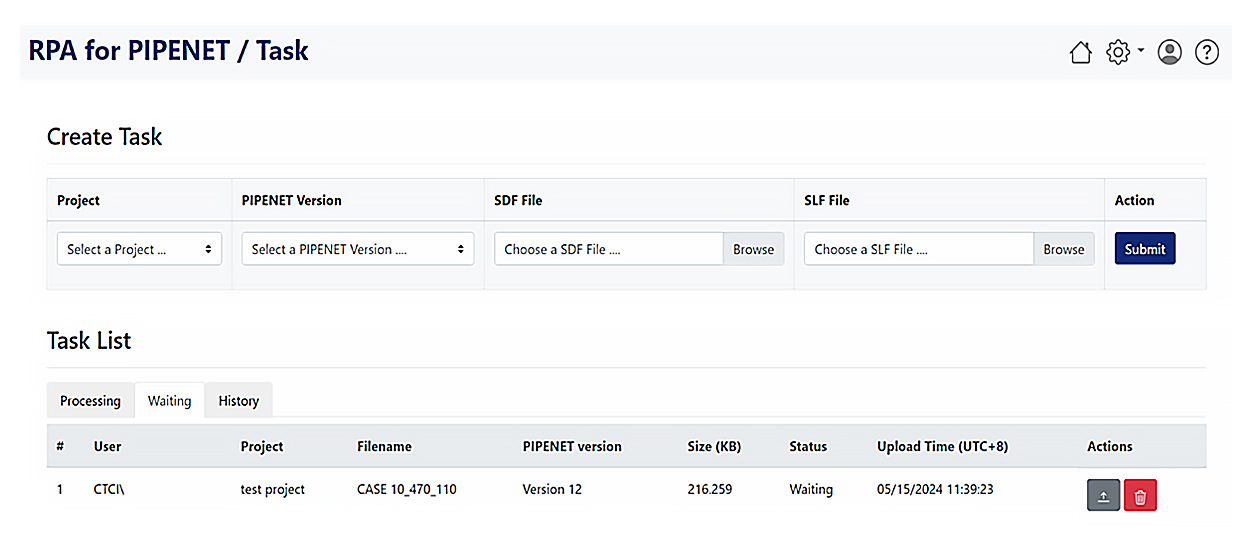
RPA for PIPENET Automation has made pipeline engineers' design process more flexible by eliminating up to 80% of the waiting time traditionally associated with simulations. This allows engineers to utilize their time more freely. During peak periods of high simulation demand, RPA can automatically distribute and schedule tasks, further boosting design efficiency. For instance, in April 2024, RPA handled 31 pipeline design simulation tasks, totaling approximately 21.5 hours of execution time. This indicates that RPA for PIPENET Automation delivers efficient and reliable service support for pipeline design, preventing engineers from idling during simulation durations and allowing design teams to focus their time on other high-value tasks. As the number of projects increase, RPA for PIPENET Automation is poised to continue delivering even greater benefits.
Application Two: MRR Automation
The Material Received Report (MRR) is a critical step in the process of inventories inspection at construction sites and recording them in the accounting system. The original MRR process involves the following steps: after materials are received and inspected by warehouse personnel, a Material Received Report (MRR) is generated in the material requirement system. This report is then uploaded to the accounting system for review by finance personnel. Once verified for accuracy, the material requirement system will complete the recognition of the materials into inventory.
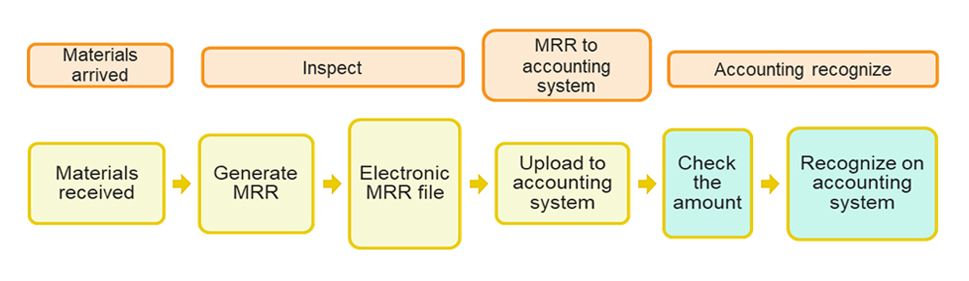
However, this process has several pain points:
• Complex multi-system workflow: The steps of MRR process are tedious and involve multiple systems. If users are not familiar with these systems, troubleshooting can consume additional time.
• Risk of human error: Manual operations at each step can lead to data errors or missing documents, causing potential risks of inaccuracy when conducting material inspections and financial recognitions.
Difficulty in tracking MRRs: The current system lacks a strict log-in policy for MRR applicants, resulting in missing information regarding the person in charge of the report. This makes tracking the MRR even harder.
Combining RPA technologies with a web-based interface can systematize the MRR process, effectively addressing the pain points of traditional workflows. Once colleagues at the construction site have logged the received materials into the inventory system, the RPA system automatically completes the subsequent steps, requiring only final recognition from the finance team. The systematized improvements include the following:
• Comprehensive automation: Previously, the process required operations across multiple systems. Now, RPA automates these operations, achieving integration between systems and eliminating the errors of manual handling..
• Verification on precise value and personnel: As the process initiates, the system automatically checks the amount of the MRR and immediately notifies relevant personnel if any issues occur. The information of the persons in charge is also automatically imported into the system by RPA for further tracking and management.
• MRR progress tracking: Users can view the current stage of each MRR in the system on the MRR Automation website, such as whether it is in the file download stage or has been uploaded to the accounting system, ensuring process transparency.
• Result notifications and report generation: After the report is uploaded into the system, the RPA system will automatically notify users via email.
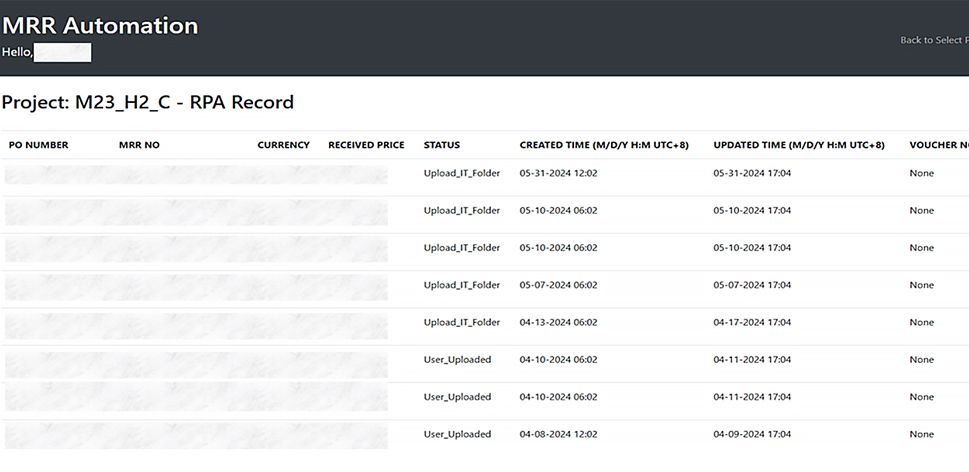
Incorporating RPA technology and a web-based interface into the MRR process has significantly improved workflow efficiency and accuracy while enhancing transparency and collaboration. This system provides a more efficient and reliable solution for material acceptance and recognition on inventories. All current projects owned by the Group have adopted the MRR Automation system. For example, over 200 MRRs were automatically processed and uploaded in April 2024. This automation replaces traditional manual tasks such as printing, signing, scanning, and uploading, accelerating the material acknowledgment process and proactively notifying users of the results. Consequently, it significantly reduces the workload for on-site personnel. Additionally, users can track the process progress on the website, increasing transparency and making it easier for relevant personnel to monitor the status.
Other Active RPA Operations
In addition to the applications mentioned above, the company has developed several RPA solutions for daily operations, further enhancing work efficiency. Here are the specifics:
• Partial Deliveries on Bulk Material: RPA automatically splits items based on data regarding each order and inputs the information into the materials management system.
• Flagging Suspended Vendors: RPA searches for blacklisted vendors on the government procurement website, compares them with the company's vendor list, and marks any violators as suspended in the vendor management system.
• Online Banking Receipt Data Download & SAP Voucher Posting: RPA login the SAP system to automatically print vouchers.
• Payment Document Generation and Conversion: RPA generates payment proposals and creates vouchers in SAP.
• Accounting Reconciliation: RPA downloads and compares received data and then performs reconciliation in the SAP system.
• Overseas Voucher Printing: RPA automatically aggregates and prints data, and organizes the printing of vouchers and attachments by region.
Outlook
In summary, the application of RPA technology holds immense potential for enhancing corporate governance and operational efficiency. Here are several feasible directions for development:
1.Automated data processing
RPA can automate data processing to ensure consistency and accuracy, reducing the risks of human errors. This not only enhances internal and external trust but also provides transparent and accurate data and reports, which are crucial for managing projects.
2.Risk management
RPA aids in monitoring and analyzing various processes, helping companies identify and address potential risks promptly. Combined with automated risk assessment, businesses can swiftly take action to mitigate risks, minimizing negative impacts on projects and operations. This is critical for engineering projects because efficient and accurate risk management is essential for the smooth completion of a project.
3.Optimized decision-making
In the past, data loss during processes could limit decision-makers to relying solely on outcomes for judgment. RPA's systematic approach ensures data integrity, providing comprehensive data support for decision-makers to optimize their decisions, further enhancing overall operational efficiency and project success rates.
Looking ahead, CTCI will continue to introduce and deepen the application of RPA technology, integrating it with sustainable development and ESG initiatives, and striving towards the ESG goal of being a Guardian of the Sustainable Earth.






