Corporate Citizen
企業公民
ECOVE’s Safety-based Technology Helps to Build Intelligent Occupational Safety & Health Management
The rapid development of technology has not only changed people's lives but has brought about industrial progress and development. ECOVE Environment Corporation (hereinafter referred to as "ECOVE"), a CTCI Group subsidiary, has invested in the energy-from-waste field for more than 20 years and is the first company in Taiwan to export its incineration technology overseas. ECOVE not only integrates and refines its technology but also keeps up with the times regarding occupational safety and health management. This article will share how ECOVE introduced intelligent applications into occupational safety and health management to create a long-term protection and security network for ECOVE's employees and fulfills commitment to "putting employee safety first."
Combining Big Data and Maintenance Management Systems to Improve the Effectiveness of Occupational Safety and Health Management
ECOVE places employee's safety and health as a top priority in its operations. To enhance occupational safety, reduce risks, and ensure the quality of environmental, health and safety control, ECOVE uses large operation data, combined with in-house Intelligent Operation and Maintenance (iO&M) system to effectively analyze, record, and manage the operation data of each plant. The iO&M system consists of several subsystems, including the Operation Results Management system (ORS), Important Operation Information (IOI), Maintenance Management Information System (MMIS), Electronic Patrol Management System (EPMS), Remote Control System (RCS), and Duty Handover Log (DHL). The MMIS, EPMS, and DHL systems digitally integrate various types of information and data from overhaul and essential operation activities such as inspection, daily handover, maintenance, and repair. The online information is available to operators, managers, and industrial safety personnel to understand site operations and confirm the equipment isolation control status. Besides, operators would be able to check the system operation records, maintenance SOPs, operation control sheets, and hazard information to effectively reduce hazard risks before, during, and after operations. Another important tool of safety management is the MMIS (Maintenance Management Information System), which has functions include operation control, control query, hazard notification, and hazard analysis. The MMIS can list control items for daily operations and confirm isolation items by informing potential hazards before operations. Using hazard analysis, we conduct toolbox talks and safety promotion, and ensure that personnel wear protective gear and work according to regulations to ensure safety during operations. This also allows supervisors to browse all operational control items of the day using the control query function for effective control and spot-check. In addition, the MMIS can systematically incorporate the occupational safety and health regulatory items in the scheduling, including automatic inspection for boilers, stationary cranes, forklifts, and other machinery and equipment, as well as the routine inspection results of EPMS (Electronic Patrol Management System). The MMIS can also schedule equipment maintenance and follow up on maintenance statuses to avoid any oversight. Besides using the iO&M system to integrate on-site safety management operations measures of each factory/plant, ECOVE continues to refine various safety protection mechanisms and measures to improve occupational safety, health management efficiency, and personnel safety. A prime example for on-site safety-based technology application is introduced in the following.
Setting up an Electronic Access Control System to Enhance Safety Management
ECOVE's primary considerations for setting up an electronic access control system at Miaoli energy-from-waste (EfW) plant are to effectively control the entry/exit of garbage trucks, the frequent entry/exit of contractors during the yearly overhaul period, and the daily access of plant personnel. The electronic access control system is able to deal with face recognition, license plate recognition, and electronic fence around the plant. The system not only controls the number of people entering the factory and confirms the identity of persons with the entry authorization list in real-time, but it can also issue alerts and video recordings through human detection cameras. Electronic access control system can receive the essential data within the optimal time for handling, control the accessibility of personnel in real-time, and manage the plant's security, enhancing control efficiency and protecting the plant's safety.
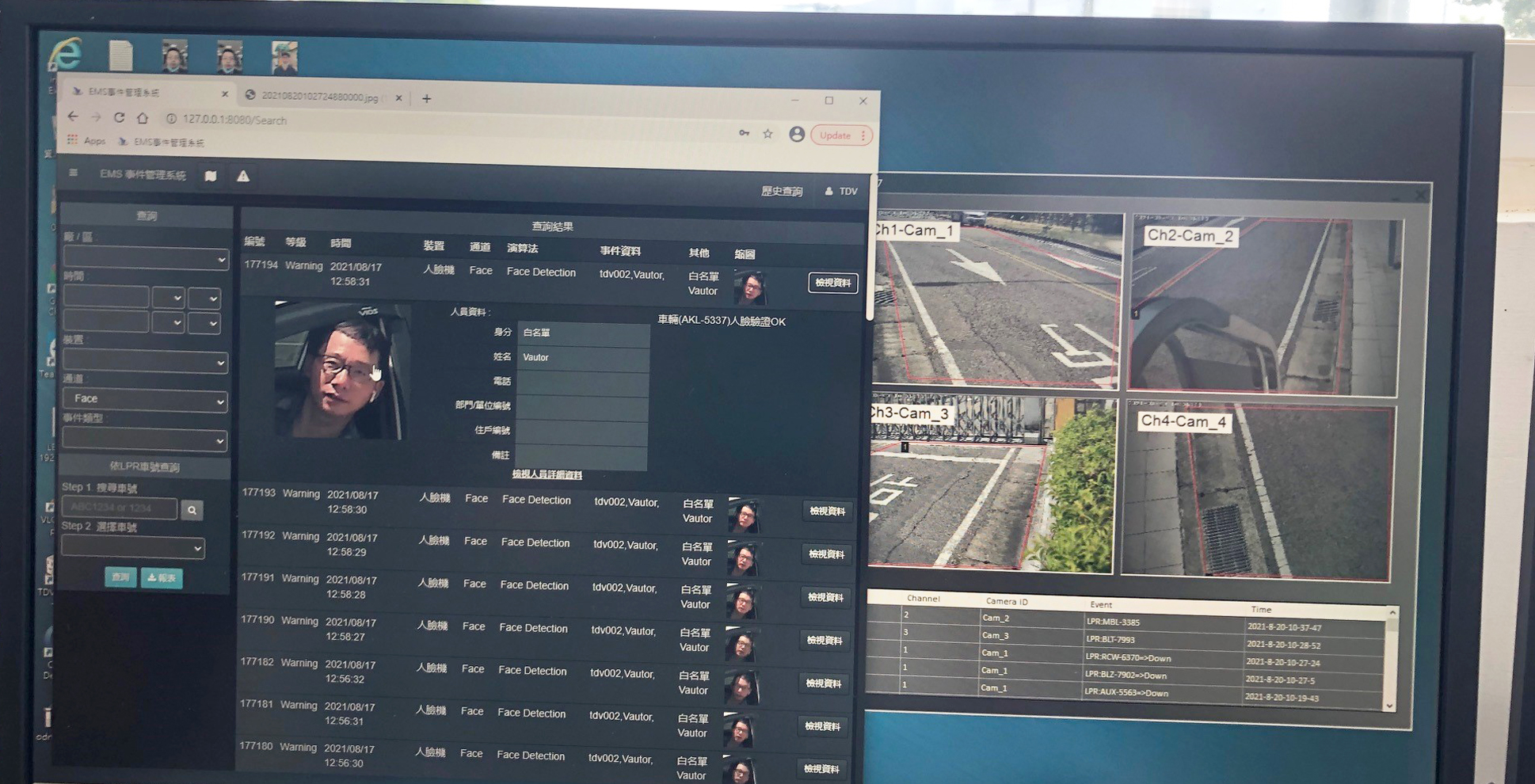
Face recognition comparison screenshot (image taken from the Miaoli EfW Plant)
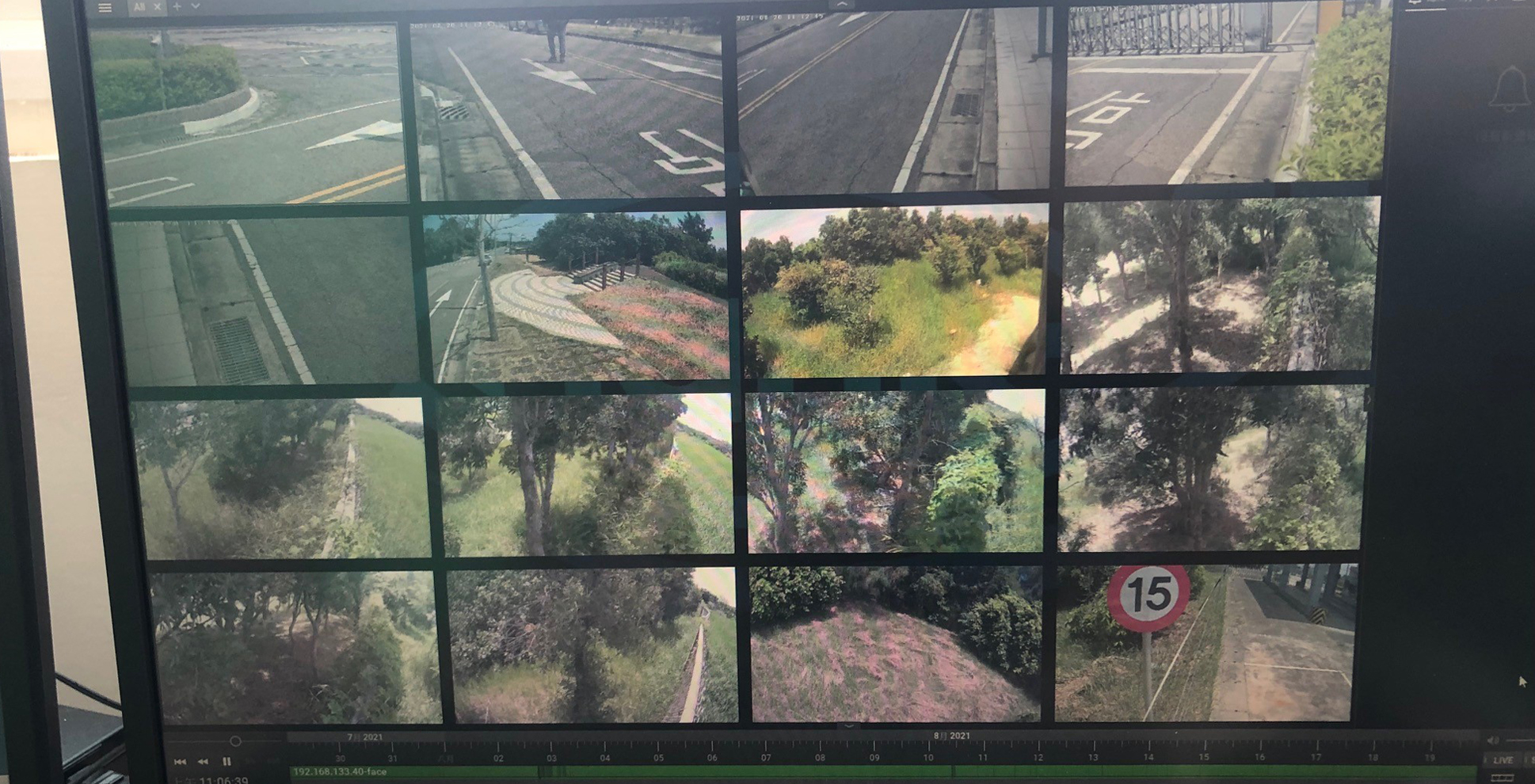

Conclusion
ECOVE strives to become "the most reliable provider of industry leading ‘resource cycling’ services." With the concept of sustainable management and the core value of being "people-oriented," we actively invest our resources to build a safe and secure workplace for our employees and promote the safety culture of "company-wide commitment to accountability." Our employees' participation in safety-related activities and training allows us to achieve health promotion and create a friendly workplace. ECOVE's safety, health, and environmental policies are based on environmental protection and creation of a safe and healthy working environment. We continue to promote and improve a healthy workplace through various programs and systems to ensure a safe and secure working environment. Besides continuous improvement and review of potential risks and hazards, ECOVE also makes good use of technology to reduce workplace accidents and enhance workplace safety through intelligent systems and a strict occupational safety and health management system, moving toward a zero-accident future.

Tainan Cheng-Hsi EfW Plant operated by ECOVE achieved a record of 16 consecutive years of zero accidents.


