Sustainable Future
永續未來
Upgrading Flue Gas Treatment System of Gangshan Energy-from-Waste Plant to Reduce Air Pollution
- Yu-Chuan Hsiao, Projects Engineer at ECOVE Environment Services Corp., CTCI's Group Resource Cycling Business
- Tien-An Yan, Projects Engineer at ECOVE Environment Services Corp., CTCI's Group Resource Cycling Business
As awareness of environmental protection becomes more prevalent, the public has been much concerned about the environmental quality and sustainability issues in living surroundings. In 2017, the Environmental Protection Administration proposed the Waste Treatment Diversification Plan (Environmental Protection Administration of the Executive Yuan Letter Ref. No. 1060177108 dated June 22, 2017), promoting the policy of life cycle extension of energy-from-waste (incineration) plants, seeking to simultaneously achieve the goals of sustainable operation of the EfW plants and upgrading air pollution control devices. ECOVE, a subsidiary of CTCI Group, respects the same sustainability philosophy and has accumulated more than two decades of experience in incineration and in electromechanical maintenance. It is the first company in Taiwan to expand incineration business overseas. Through relentless refinement of technologies, equipment improvement, and the introduction of intelligent operation and management systems, ECOVE improves resource cycling efficiency and reduces environmental impact. To achieve the goal of reducing air pollution emission and being more sustainable, it actively adopts new technologies in the life cycle extension projects of incineration plants, and reviews and optimizes processes with operational experience.
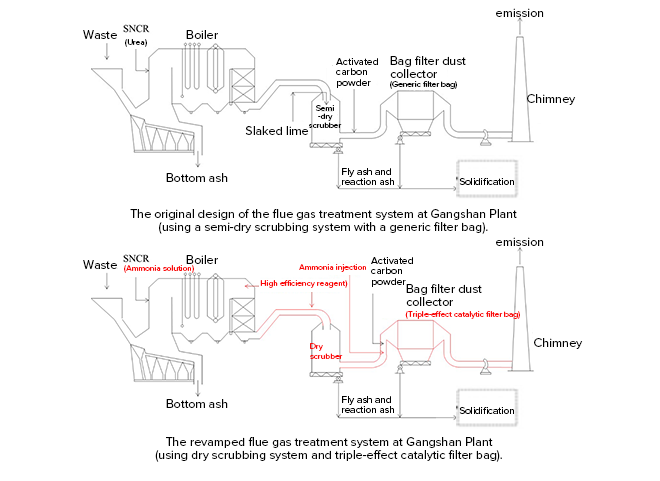
The Gangshan EfW Plant (hereinafter referred to as the Plant) has been in operation for over 20 years and needs a replacement of old equipment. When the selection of equipment is concerned, it is a must to consider introducing new technologies that can yield air pollution reduction benefits through process optimization in addition to extending the service life cycle of the Plant. Therefore, in the Reconstruction-Operation-Transfer (ROT) plan for the Plant, ECOVE integrated years of operational experience and the skills of equipment improvement personnel from multiple plants for a thorough evaluation. Then, an improvement plan was proposed for the bag filter dust collector in the flue gas treatment system. The bag filter dust collector and flue gas duct (from the outlet section of the economizer to the inlet section of the chimney) were replaced while generic filter bags were replaced with a new triple-effect catalytic filter bags. Besides, the chemical usage for flue gas treatment was also reviewed in order to reduce air pollution.
Improve the Overall Planning of Air Pollution Emission Reduction and Waste Gas Treatment System
Of the 24 waste incineration plants in Taiwan, ECOVE has operated, managed, overhauled and carried out system upgrades on two thirds of them. ECOVE knows well different furnace designs of incineration plants, and can provide tailor-made equipment upgrades and efficiency improvement planning services. In view of the revamping of the Plant, the issues need to be addressed for the existing flue gas treatment system in the Plant included: new process integration planning, equipment disassembly and assembly spaghetti diagram, isolation planning of the old system, integration of new process and coordination with regional waste scheduling restrictions, etc. In light of these daunting issues, ECOVE proposed a series of flue gas treatment solutions (as compared with the figure below) to achieve energy saving, emission reduction and other benefits. The explanation is as follows
.During the design phase, with the aim of hitting the air pollution reduction target, a new triple-effect (dust removal, nitrogen oxides removal, and dioxin removal) catalytic bag filter technology was adopted after evaluation. This enabled the decomposition of nitrogen oxides and dioxins over and above having traditional bag dust removal function. ECOVE optimized the process based on past operational experience by changing the reducing agent of the nitrogen oxides removal system and reducing the amount of activated carbon used in the dioxin removal system.
.To operate the new triple-effect catalytic bag filter at the most suitable reaction temperature and prevent further reaction between residual ammonia and sulfur oxides in the flue gas to generate ammonium bisulfate (ABS) which can result in the poisoning of the catalyst filter bag, the plan was to change the semi-dry scrubbing system to a dry scrubbing system, and use high-efficiency reagents to increase the temperature of the flue gas before entering the bag filter dust collector by reducing water injection.
.A two-stage injection of high-efficiency reagents before the semi-dry scrubber effectively reduced the concentration of sulfur oxides entering the bag filter dust collector and prevented the generation of ABS. And then an ammonia injection system was installed at the flue gas duct before the bag filter dust collector.
.As for the project management, armed with the experience of conducting system upgrades for multiple plants, ECOVE analyzed the shared system pipelines and equipment, then conducted pre-isolation operations and hypothetical works in order to lay out phased construction (including operation phase and single furnace shutdown). Ultimately, it grasped the critical path connectors of the construction period to strive for maximum construction efficiency, shorten shutdown time, hence reducing the impact to regional waste scheduling.
New Technologies Introduced to Nitrogen Oxides Removal System
The original design of the Plant's nitrogen oxides removal system was an SNCR (Selective Non-Catalytic Reduction) system using urea as a reducing agent. The triple-effect catalytic filter baghouse technology was introduced to further reduce emissions. Based on ECOVE's experience of conducting operation and overhaul for various incineration plants, the existing SNCR supply system was replaced with a new one which was complemented with an ammonia solution injection system in front of a bag filter dust collector to make the triple-effect catalytic filter bag work effectively. After the revamping, the hourly average emission level of nitrogen oxides is estimated to reduce from 105 to below 30 ppm, with a reduction rate of 71%.
Dioxin Removal System Upgraded, Reducing the Amount of Activated Carbon Powder
The original design of the activated carbon powder process used by the Plant was to inject activated carbon into the front end of flue gas duct of the bag filter dust collector to adsorb trace heavy metals (such as mercury) and dioxin in the glue gas. Then, when the flue gas passes through the filter bag, the activated carbon powder and dust that have adsorbed pollutants are sieved out and removed by the filter bag.
In this project, ECOVE utilized a triple-effect catalytic bag filter system to reduce the use of activated carbon powder used at the front end, and the remaining dioxin can be decomposed through the triple-effect catalytic filter bag. After the revamping was completed, the amount of activated carbon is estimated to be reduced from 0.61kg per ton of waste to 0.12kg per ton of waste, and the emission level for dioxin detected is estimated to be reduced from 0.1 to below 0.05 ng TEQ/Nm³. Based on the Plant’s annual processing capacity of 370,000 metric tons of waste, approximately 181.3 metric tons of activated carbon powder can be reduced annually.
Two-stage Dry Scrubbing System, More Efficient Reagents
The existing scrubbing system in the Plant is a commonly found semi-dry scrubbing system, where the slurry slaked lime is injected into the semi-dry scrubber through an atomizer for deacidification. With an eye toward maintaining the flue gas temperature at the optimal reaction temperature of the triple-effect catalytic filter bag (above 200℃), ECOVE adopted a dry scrubbing system based on the experience of operating and testing in multiple plants, as well as repeated reviews of the air pollution prevention and control equipment process. At the same time, ECOVE actively tested and analyzed the dry scrubbing reagents for selection of the reagent and the location of injection points. A two-stage scrubbing system was thus proposed, where reagents were injected into the flue gas duct of the economizer and before the dry scrubber respectively. After the completion of the revamping, the hourly average emission level for hydrogen chloride and sulfur oxides are estimated to be reduced from 25ppm and 30ppm to below 10ppm and 8ppm, respectively, with emission reduction rates of 60% and 73%.
Deliver the Most Reliable Service towards the Goal of Air Pollution Emission Reduction
Looking forward to the future, ECOVE, as a practitioner of resource cycling, endeavors to actively integrate practical experience in incineration operations and constantly introduce new technologies through the improvement of resource cycling efficiency. We hope to further review and optimize the existing processes during the equipment upgrading for service life cycle extension of incineration plants and the introduction of new technologies for air pollution reduction, so as to gradually achieve the goal of air pollution reduction for more sustainable operations. ECOVE also actively engages in national and regional environmental agendas and policies. By participation in various projects from local governments and central authorities, we deliver innovative technical solutions based on rich project experiences. We will continue to contribute to environmental protection, protect the global environment, and realize the vision of becoming “the most reliable provider of industry-leading ‘resource cycling’ services."

