Technology
技術分享
Industrial Application of Robotic Process Automation
— Leo Hu, RD Engineer at Research & Innovation Center, CTCI Corp., Group Engineering Business
Digitization and process automation are the key steps for CTCI Group to realize intelligent operations. Through the execution of a computer process called Robotic Process Automation (RPA) technology, operations that rely on manual input and maintenance will be transformed into digitalized data. That way, it will free colleagues from mechanized and repetitive tasks, creating more values for enterprises with advanced uses of the digitalized data.
The Importance of RPA
In a report called “Top Ten Strategic Technology Trends in 2020” released by Gartner, an international market research agency, it mentioned the concept of “hyperautomation.” The goal of hyperautomation is to use a variety of artificial intelligence and machine learning models to complete tasks that originally required humans to perform. However, currently there is yet any tool that can completely replace humans’ independent operations. We can only use RPA to connect the existing conventional systems, which allows users to get the automated data simply by importing and exporting them, and through artificial intelligence (AI) and intelligent business process management systems (iBPMs), we can enjoy decision-making with the assistance of AI. In short, RPA is an important preliminary tool for enterprise digital transformation and efficiency improvement.
What is RPA?
RPA, which stands for Robotic Process Automation, can be considered as a software robot that automatically operates other applications according to a set script. For example, if you want to turn the 1,000 contacts in your phone directory into a table list, will take a lot of time if you do it manually. But through RPA, all you need is to know what columns need to be copied, and which location on the form the data should be pasted. Then, RPA will complete the form automatically.
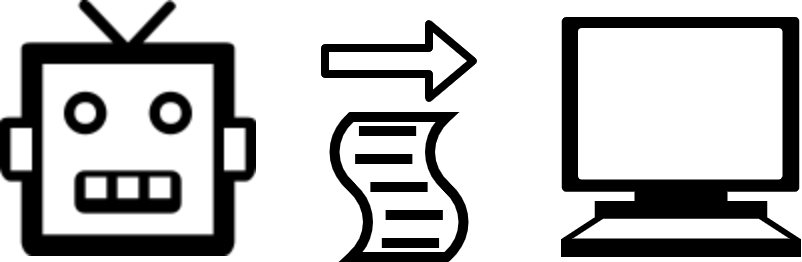
The robot operates the computer according to the script.
RPA’s Role in Relation to Other Systems
RPA is seen as a bridge between application software in that it can connect business systems to other software, such as Excel, professional design software, and web interfaces, which are usually not equipped with available Application Programming Interface (API) for data exchanges, and thus requires window-like graphical user interface (GUI) to carry out operations. With the help of RPA, however, GUI work that formerly must be performed manually can now be done automatically.

RPA can bridge different software.
The Procedure of Using RPA Software
The main procedure of using RPA is as follows: 1. Establish a development environment Install the software development tool that can help design RPA script file on a computer where operations are intended to be automated. 2. Design RPA script file Carry out process analysis and settings on the processes and needs that you wish to be automated so that the actions which were originally done manually gradually become RPA script files. There may be some process obstacles caused by the limitation of robot functions that need to be eliminated. 3. Set the execution environment and execute the RPA script file Install and execute the robot execution software and run robot script file on the computer where a given operation is intended to be automated. 4. Manage RPA with management tools Control the operation of the robot and observe the execution results to make appropriate corrections.
RPA Usage Scenarios
As long as it involves standardized operations, such as data input, correction, verification, and output for the business systems, RPA is a suitable tool. For example, when you need to input a manufacturer list into the business management system, or you want to check whether the entries in the file are the same as those in the business system, RPA will come in handy. Depending on the characteristics of different business systems, there are several usage scenarios for RPA: 1. Batch processing of data in the business system Import and export data into/from the business system in batches by RPA. 2. Interconnection of different applications When operating across systems, RPA can serve as a bridge for information exchange. 3. No available business system When no business system is available and colleagues can only handle tasks manually, the RPA can help standardize and automate the operation process.
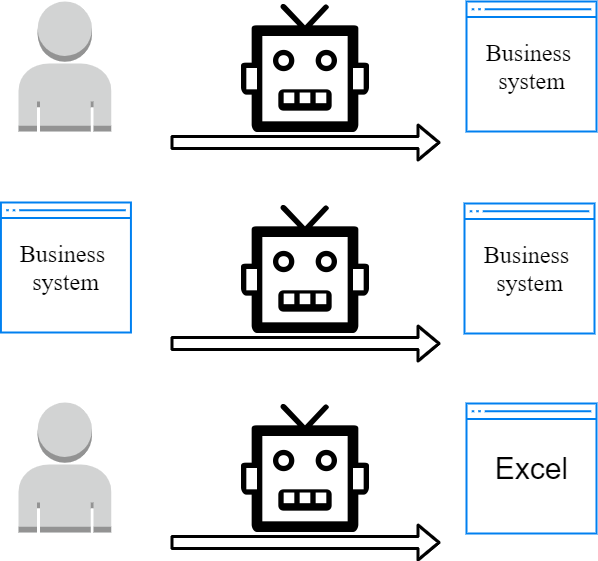
Three usage scenarios of RPA.
Advantages of Using RPA
1. Optimize human resources RPA allows colleagues who were originally engaged in highly repetitive and mechanized operations to perform more valuable works, gives full play to the value of manpower, and at the same time increases the enterprise’s output value. 2. Increase processing power Utilizing RPA software for automatic execution of any given task considerably enhances the processing power, allowing it to deal with a large quantity of data simultaneously. If there is a sudden increase of data that needs to be processed, it can be easily handled to avoid temporary manpower shortage. 3. Reduce costs As RPA increases processing efficiency, costs will be reduced. 4. Standardize processes Turning processes that originally relied on manual operations into fixed-program operations can reduce the dependence on individuals and over time helps the company enhance its organizational strength.
Related Technologies
RPA is often compared with other technologies or can work in unison with them. The common technologies are as follows: 1. The difference between RPA and Office macro Office macros and RPA are both automated information processing tools. They are similar in the way that both tools help automate the steps that would have been done manually. The difference is that Office macro can only be used in Office series products, such as Word, Excel, PowerPoint, while RPA can span various applications. 2. Optical Character Recognition (OCR) and its benefits OCR is a technology that reads handwritten or printed text optically and converts it into textual information. One of the common applications is the business card scanning software, which can automatically retrieve information such as name, phone, and email after scanning the card without any need for manual input. OCR technology can work with RPA to process non-digital documents (such as scanned documents) and convert them into processable text data. However, the recognition success rate of OCR technology is not perfect, and it still needs to be checked according to data rules or manually. But even so, the efficiency can still be greatly improved compared to complete manual input. 3. Artificial Intelligence (AI) RPA can help collect data for AI, and AI can in turn assist RPA during RPA implementation process. When RPA encounters difficulties to make judgements or when ambiguous rules exist, it can use AI to assist it making judgment. Once RPA has been operating for a period of time, we can also utilize AI to analyze the characteristics of data processed during operation and predict future trends.
Scenarios Where RPA Are Inapplicable
The following are common scenarios where RPA is not applicable: 1. Data with irregular patterns or non-digital data Data with irregular patterns include random task assignments and meeting minutes, which are conversational records in nature. An example of non-digital data is manuscript. 2. Data that is not repetitive in nature and require flexible processing For a process that changes frequently, there will be no set rules for RPA to follow. Examples include replying customer letters and maintaining customer relationships. 3. Work that requires considerable manual judgment Jobs that require specific knowledge and experience, such as engineering design, art design, and etc. 4. Processes with little data or are only executed occasionally The economic benefits of developing RPA for such operations may not be significant enough.
RPA Applications in CTCI Group
CTCI Group has introduced RPA into its daily accounting works, successfully decreasing the amount of time needed for online bank receipts and payment uploads, receivable voucher reconciliation, and overseas voucher printing, effectively saving 40-67% of daily operation time. At the same time, we are evaluating the possibility of applying RPA to repetitive operations in other areas of the Group, including automatic archiving of scanned project documents, massive repeated transcoding in design work, data transfer across design software, delivery information that involves shipments and order quantities, linking accounts between various companies in the Group, report production and printing for audit work, etc. Depending on the different operational characteristics of each field, RPA design requirements will also vary. To introduce RPA to an existing operational process, one needs to specify the current work method and the desired areas of tasks which could be assisted by RPA, so that RPA experts can help to evaluate whether and how RPA could be availed to achieve operational efficiency improvement across departments. The introduction of RPA as a new IT technology to various departmental functions would help to reduce the amount of time needed for colleagues to perform repetitive and tedious operations. Not only does this improve work efficiency, but it also improves job satisfaction among staff, creates more work value, and hence increases employees’ happiness. IT technology, if used rightly, would become a perfect assistant for everyone for processing day-to-day works.
